Dequeue Interface in Java
In the previous blog, we learned about Queue Interface in Java. If you want to know more about it visit Queue Interface in Java. In this blog, we will go through the subtype Queue Interface i.e. Dequeue interface.
Dequeue Interface
Dequeue stands for double-ended Queue, meaning we can add or delete elements from both ends of the data structure. Due to this reason, Dequeue can be used as a stack or queue. As we know the stack follows the Last in First Out (LIFO) approach and the queue follows the First in First Out (FIFO) approach. It supports both approaches. Dequeue is present in java.util package.
Syntax of Dequeue
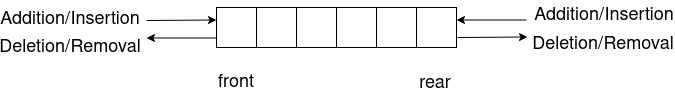
Working of Dequeue
As we have already seen in our previous blog, Queue elements are added from rear and deleted from front. The advantage of Deueue is that we can insert or remove elements from both front and rear.
Program to demonstrate Dequeue
Output
Methods of Dequeue
- add()
- addFirst()
- addLast()
- offer()
- offerFirst()
- offerLast()
- getFirst()
- getLast()
- peekFirst()
- peekLast()
- removeFirst()
- removeLast()
- pollFirst()
- pollLast()
add() method inserts or adds the element to the end of the Dequeue only if there is space. But if the Dequeue is full and there is no space for the element, it throws an exception called IllegalStateException. It returns true when the insertion or addition is successful.
e.g.
Output
addFirst() method adds or inserts the element passed in the parameter to the front of the Deque if there is space. But if the Dequeue is full and there is no space for the element, it throws an exception called IllegalStateException. It returns true when the insertion or addition is successful.
e.g.
Output
addLast() method inserts or adds the element to the end of the Dequeue only if there is space. But if the Dequeue is full and there is no space for the element then it throws an exception called IllegalStateException. It returns true when the insertion or addition is successful.
e.g.
Output
offer() method adds or inserts an element at the tail of the queue. This method is the same as add() method but the difference is, it does not throw an exception when the capacity of the container is full instead it returns false.
e.g.
Output
offerFirst() method adds or inserts an element at the head of the queue. This method is the same as the addFirst() method but only the difference is, this method does not throw an exception when the capacity of the container is full instead it returns false.
e.g.
Output
offerLast() method adds or inserts an element at the tail of the queue. This method is the same as add() method but the only difference is, this method does not throw an exception when the capacity of the container is full instead it returns false.
e.g.
Output
getFirst() method returns the first element of the deque. If the deque is empty then it throws an exception
e.g.
Output
getLast() returns the last element of the deque. If the deque is empty, an exception is thrown.
e.g.
Output
peekFirst() returns the first element of the deque. If the dequeue is empty then it returns null
e.g.
Output
peekLast() returns the last element of the deque. If the dequeue is empty then it returns null.
e.g.
Output
removeFirst() method returns and removes the first element of the deque. If the deque is empty, an exception is thrown.
e.g.
Output
removeLast() method returns and removes the last element of the deque. If the deque is empty, an exception is thrown.
e.g.
Output
pollFirst() returns and removes the first element of the deque. If the deque is empty, the method returns null.
e.g.
Output
pollLast() returns and removes the last element of the deque. It returns null if the deque is empty.
e.g.
Output